
SELF SUSTAINMENT SYSTEM
The "Self Sustainment System" (S.S.S. in short) is the official production system advocated by Project Autopia.
It is an absolutely fundamental feature of a Selfed, and no individual or community can be considered a complete without it.
An S.S.S. is defined as any collection of devices specifically designed in order to be able, as a whole, to grant their owner the ability to obtain anything he could possibly need to live entirely by himself, with no reliance on external resources, and for an indefinitely long period of time.
Composition
A complete S.S.S should be composed by:
- a certain number of production devices
- a certain number of recycling devices
- an autonomous energy generating device
There is no fixed number of devices of which a complete S.S.S. should be composed; the fundamental rule is that, for every possible need, there shall be a device able to produce it, and a device able to return its scraps to the raw materials it was produced from; in addition, there shall be an energy generating device to keep them all in operation.
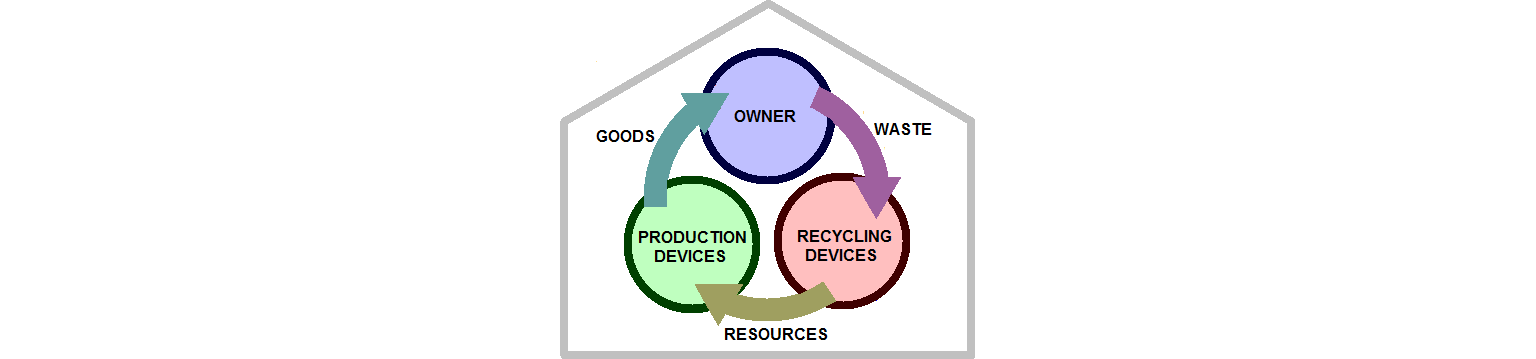
simplified scheme of an S.S.S.
Kernel
Since the S.S.S. is designed to work for an indefinitely long period of time, it needs to deal with the inevitable degradation or accidental damaging of its own components, by replacing them with new ones. For this reason, a sub-set of production devices shall be designed with the purpose of producing more S.S.S. devices including themselves (in other words, the S.S.S. shall be self-replicable); this sub-set is called the "Kernel" of the S.S.S..
Since the degradation/damaging might happen to the Kernel components themselves, any S.S.S. should have at least 2 copies of its Kernel, so that each one of them can be promptly replaced by the other.
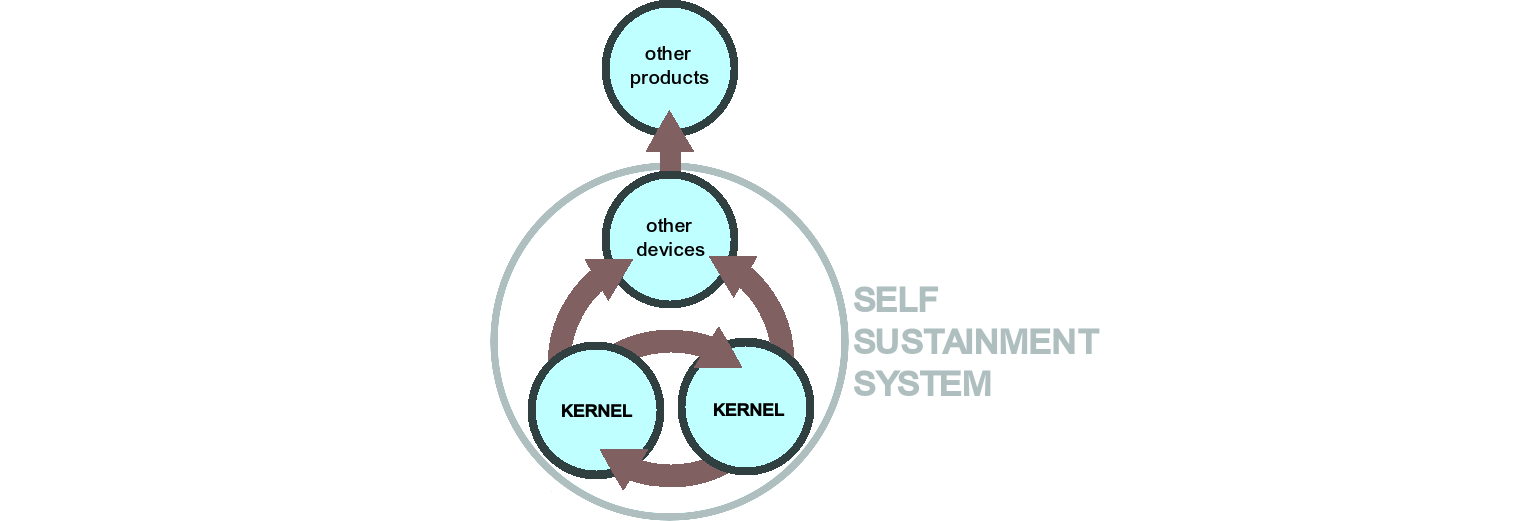
scheme of an S.S.S., showing the function of the Kernel
Operation
Any S.S.S. operates through a cycle articulated in 3 phases:
1) Any good is entirely produced by its future consumer through the specifically designed production devices owned by him
2) The goods are consumed by their producer, which turns them into trash
3) Through specifically designed recycling devices, any generated waste is turned by the owner into the same raw materials from which the respective good was produced
The only exception to this rule is energy, which because of physical reasons (2nd law of thermodynamics) cannot be entirely recycled; however, it can still be produced by autonomous means in accordance to the self-sufficiency principles of Project Autopia.
Principles
In order to work as intended, an S.S.S. should be designed according to the following requirements (in order of importance):
Omni-comprehensiveness
An S.S.S. must be able to satisfy any possible human need: for each possible human need, there must be a device able to satisfy it. For this purpose, each device should be designed in order to be able to serve as many purposes as possible.
Efficiency
An S.S.S. must have an output rate high enough to completely satisfy the daily requirement of its user; this is especially important in the case of biological needs (like water, food, etc.).
User-control
An S.S.S. and its component devices must be designed in order to grant their user the complete control over it.
Inter-mutuality
Each device must be designed not as a stand-alone, but rather as a complement to its reciprocal ones (i.e.: production devices to recycling devices, and vice-versa): it must be designed in order to be able to entirely process the output of its reciprocal ones, while simultaneosly produce an output that can be entirely processed by them.
Inter-replicability
An S.S.S. must be able to produce perfect copies of itself: there must always be a subset of devices able to replicate every S.S.S. device in its entirety, including themselves. For this purpose, a proper S.S.S. should always have at least 2 copies of each device belonging to said subset, so that the accidental breakdown of a device doesn't compromise the whole system.
Portability
Each device must be designed so that it can be carried around as easily as possible.
Automation
Each device must be able to work requiring the least possible amount of human intervention.
Customizeability
Each device must be able to allow the highest possible degree of personalization in terms of what it does and how it operates.
User-friendliness
Each device must be designed in order to be as easy as possible to use.
Model
This section describes a simplified ideal model of a domestic-class S.S.S..
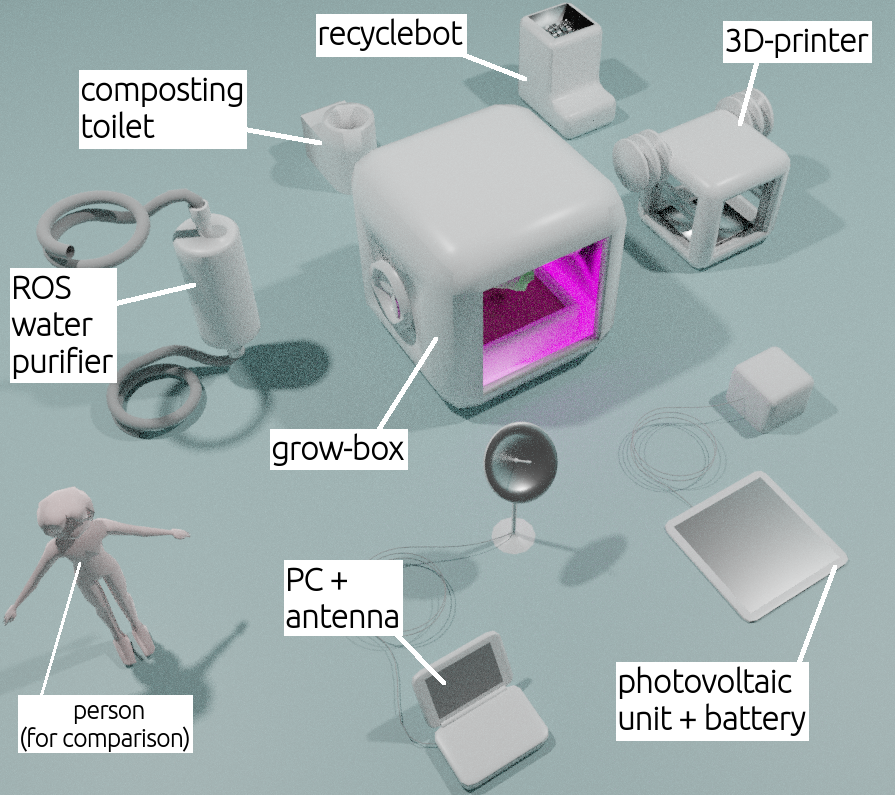
The basic components of a S.S.S.
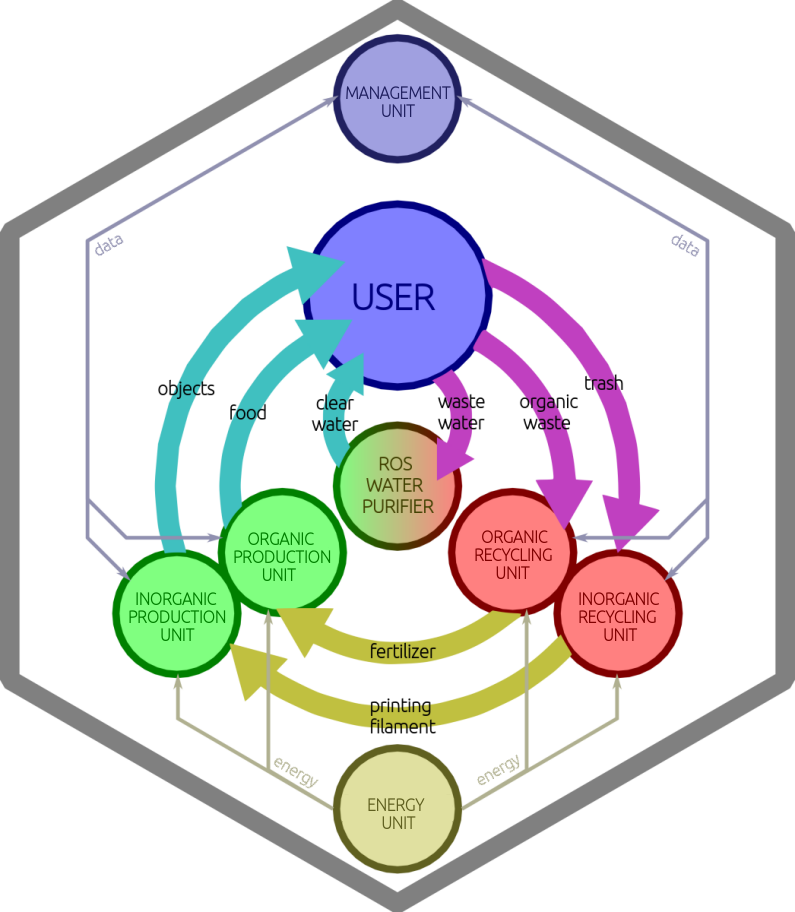
The relationships between the various components of a S.S.S.
Water Purifying Unit
Purpose: Producing pure drinkable water.
Input: Waste water, urine.
Output: Pure water.
Possible technologies: Reverse osmosis.

Organic Production Unit
Purpose: Producing food.
Input: Water, fertilizing agents.
Output: Edible plants, algae or fungi.
Possible technologies: Grow-boxes, hydroponics, aquaponics.
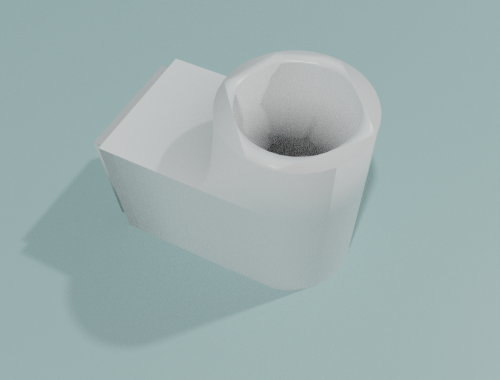
Organic Recycling Unit
Purpose: Producing fertilizing agents for the Organic Production Unit.
Input: Food wastes, dust, excrements, corpses.
Output: Fertilizing agents.
Possible technologies: Composting.
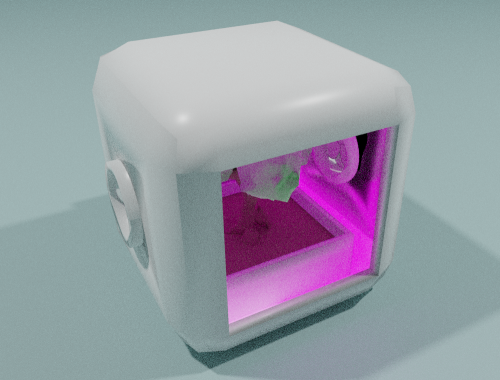
Inorganic Production Unit (*2)
Purpose: Producing objects/devices and their components (including those of the S.S.S. itself). This is a Kernel device.
Input: Plastic, metal, dyes.
Output: Furniture, cutlery, shoes, clothes, toys, artworks, musical instruments, mechanical devices, electronic devices, S.S.S. components.
Possible technologies: 3D-printing (Fused deposition modeling, Multi-material inkjet printing, Metal laser sintering).
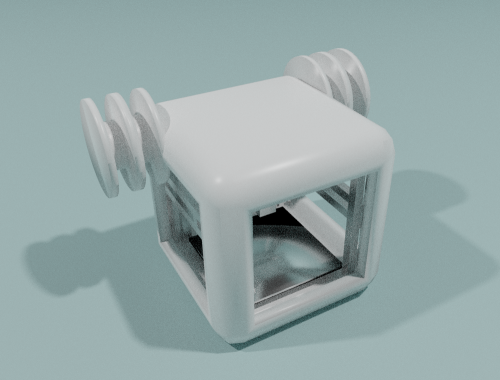
Inorganic Recycling Unit
Purpose: Producing raw matter for the Inorganic Production Unit.
Input: Trash.
Output: Plastic, metal, dyes.
Possible technologies: Recyclebots, plasma atomization.

Management Unit (computer)
Purpose: Management of other devices, personal use, website hosting, mesh networking. This is a Kernel device.
Input: Data.
Output: Data.
Possible technologies: Computer.

Energy Unit
Purpose: Producing and storing the energy required by all other devices.
Input: Renewable energy.
Output: Electric power.
Possible technologies: Photovoltaics, wind turbines.

Extension
S.S.S.s are divided in various classes based on the scope of their products's use, and the consequent amount of people for which they're intended.
Domestic Class S.S.S.
Scope: any given house
Subject: the resident individual
The most fundamental class of S.S.S., on which all the other are based. Each one of them is owned by a single individual, and designed for his personal necessities (water, food, clothing, tools, furniture, etc.)
Urban Class S.S.S.
Scope: any given city
Subject: the city's community
Designed for public services (buildings, streets, public parks, etc.). Owned and managed by all the people of a single city.
Statal Class S.S.S.
Scope: any given nation
Subject: the nation's people
Designed for projects on national scale (highways, etc.). Owned and managed by all the people of a single nation.
Global Class S.S.S.
Scope: the entire planet
Subject: the whole mankind
Designed for projects on an international or global scale (world wide webs, etc.). Owned and managed by all the people on the planet.
Return